
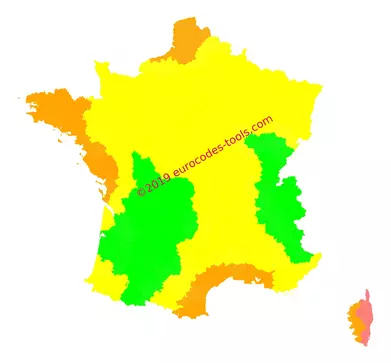
What are the French wind zones according to Eurocode 1 (NF EN 1991-1-4/NA) ?
On the map of the national annex, the French metropolitan area is divided into four wind zones identified from 1 to 4. Amendment A3, published in April 2019, replaces the division by cantons into a division by municipalities.
| Zone | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fundamental value of the basic wind velocity vb,0 | 22m/s | 24m/s | 26m/s | 28m/s |
The French overseas departments, overseas territories and overseas collectivities each have a specific basic wind velocity.
| Zone | French Guiana | Mayotte Island | Martinique Island | Reunion Island | Guadeloupe Island |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fundamental value of the basic wind velocityvb,0 | 17m/s | 30m/s | 32m/s | 34m/s | 36m/s |
| Zone | New Caledonia | Wallis and Futuna | Saint Martin | Saint Barths | Saint Pierre and Miquelon |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fundamental value of the basic wind velocity vb,0 | 36m/s | 41.2m/s | 36m/s | 36m/s | 36m/s |
Wind zoning of Metropolitan France (2019-2024)
How to adjust the basic wind velocity for each direction of wind and according to return period in France ?
\[\displaystyle v_{b} = c_{prob} \cdot c_{dir} \cdot v_{b,0}\]- A variation have to be considered with the probability factor Cprob.
- When the wind comes from a direction where the probability of occurrence of strong winds is less, a reduction can be considered with the directional factor Cdir.
- You should also take in account the effect of the roughness of the terrain (vegetation / urbanization) and the effect of orography (terrain relief) to accurately determine the peak velocity pressure for each wind direction.
Quelles sont les catégories de terrain en France ?
0 :


Sea or coastal area exposed to the open sea; lakes and water bodies covered by wind over a distance of at least 5km.
II :


Open field, with or without a few isolated obstacles (trees, buildings, etc.) separated from each other by more than their height x40.
IIIa :


Campaign with hedges; vineyards; grove; sparsely populated.
IIIb :


Urban or industrial areas; dense grove; orchards.
IV :

Urban areas with at least 15% of the surface is covered with buildings whose average height is greater than 15m; forests.
Particularity concerning New Caledonia
Wind zoning of Metropolitan France (2019-2024) The terrain categories have been transposed to Caledonian landscapes. The reference to terrain category IV is removed and categories 0 to III of standard NF EN 1991-1-4 are illustrated by the photographs below :
0 :

Sea side.
II :

Open field.
IIIa :

Campaign with hedges.
IIIb :

Industrial areas.
Source : RCNC
Example of results given by the software Eurocodes Zoning
B1 – Localization
- Coordinates in World Geodetic System 1984 (WGS84) 3.5332°, 45.7153°
- Coordinates in French Geodetic System 1993 (Lambert 93) 741482m, 6512993m
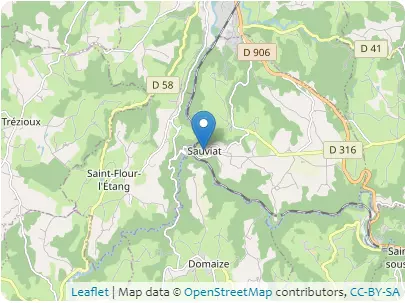
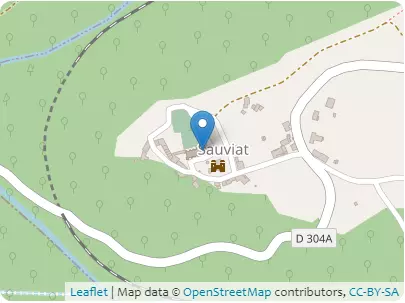
Address D 304A, 63120 Sauviat, Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes
B2 – Altitudes
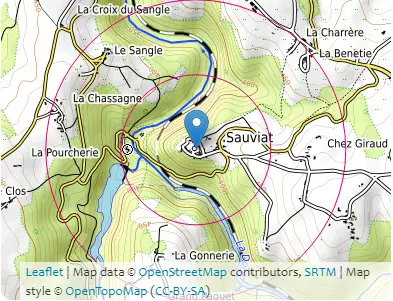
| Distances / Direction | At the place of construction | 500m | 1000m |
|---|---|---|---|
| North | 436 m | 360m | 407m |
| Northeast | 405m | 465m | |
| East | 456m | 473m | |
| Southeast | 419m | 446m | |
| South | 449m | 476m | |
| Southwest | 432m | 411m | |
| West | 360m | 468m | |
| Northwest | 403m | 452m |
B3 – Building
- Type of building: monumental building
- Design working life category: 100 years
- Max height: 15.0 m
- Orientation from North: 80°
B4 – Terrain categories
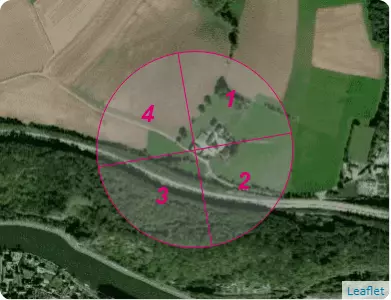
| Sectors | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Categories | IIIa | IV | IV | IV |
C1 – Snow
NF EN 1991-1-3/NA (may 2007) + A1 (july 2011)
- Zone : A2(sk,0 = 0.45 kN/m²)
- Criteria for zoning : PUY-DE-DOME (63)
- Characteristic value of snow on the ground at the relevant site : sk,436 = 0.686 kN/m²
- Ground snow load with a return period of 100 years : s100 ans = 0.774 kN/m²
- Design value of exceptional snow load on the ground : sad = 1.0 kN/m²
C2 – Vent
NF EN 1991-1-4/NA (march 2008) + A1 (july 2011) + A2 (september 2012) + A3 (april 2019)
- Zone : 2(vb,0 = 24.0 m/s)
- Criteria for zoning : PUY-DE-DOME (63)
- Zone cdir : 1
| Sectors | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sector definition | from 35 ° to 125 ° | from 125 ° to 215 ° | from 215 ° to 305 ° | from 305 ° to 35 ° |
| Fundamental value of the basic wind velocity vb,0 | 24.0m/s | |||
| Shape parameter K | 0.2 | |||
| Exponent n | 0.5 | |||
| Annual probability of exceedence p | 0.01 | |||
| Probability factor cprob | 1.038 | |||
| Directional factor cdir | 0.7 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Basic wind velocity vb | 17.4m/s | 24.9m/s | 24.9m/s | 24.9m/s |
| Reference roughness length z0,II | 0.05m | |||
| Roughness length z0 | 0.2m | 1.0m | 1.0m | 1.0m |
| Terrain factor kr | 0.209 | 0.234 | 0.234 | 0.234 |
| Height above ground z | 15.0m | |||
| Minimum height zmin | 5.0m | 15.0m | 15.0m | 15.0m |
| Roughness factor cr(z) | 0.904 | 0.635 | 0.635 | 0.635 |
| Orography factor * co(z) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Mean wind velocity vm(z) | 15.8m/s | 15.8m/s | 15.8m/s | 15.8m/s |
| Turbulence factor kl | 0.97 | 0.854 | 0.854 | 0.854 |
| Standard deviation of the turbulence σv | 3.544m/s | 4.989m/s | 4.989m/s | 4.989m/s |
| Turbulence intensity Iv(z) | 0.225 | 0.315 | 0.315 | 0.315 |
| Air density ρ | 1.225kg/m3 | |||
| Exposure factor ce(z) | 2.102 | 1.292 | 1.292 | 1.292 |
| Peak velocity pressure qp(z) | 392.0N/m2 | 491.5N/m2 | 491.5N/m2 | 491.5N/m2 |
| Peak wind velocity for Serviceability Limit States vp(z),SLS | 91.1km/h | 102.0km/h | 102.0km/h | 102.0km/h |
| Peak wind velocity for Ultimate Limit States vp(z),ULS | 111.5km/h | 124.9km/h | 124.9km/h | 124.9km/h |
Here, the orography factor is calculated according to Procedure 1, for an orography consisting of obstacles of various heights and shapes. This type of orography is the most frequently encountered.However, if the building is in a case of orography consisting of well individualized obstacle (isolated hills and ridges or cliffs and escarpments) the orography factor must be calculated according to the procedure 2. According to EN 1991-1-4 §4.3.3(1), the calculated orography factor (1.018) is not taken into account because it does not increase wind velocities by more than 5%.
C3 – Seism
Code of the Environment – Article D563-8-1 (09/01/2015)
JORF n°0248 du 24/10/2010 texte N°5
- Zone : 3(1.1 m/s²)
- Criteria for zoning : Sauviat, Puy-de-Dome (63)
- A seismic analysis may be required for this building.